General Dentistry in Cupertino, CA

It is crucial for you and your loved ones to visit your general dentist on a regular basis. When you visit your dentist for routine examinations and cleanings, our dental team can catch early signs of decay or even prevent decay from ever occurring. When small oral health issues like tooth decay go too long without being treated, they can become more serious problems like gum disease. You can protect your health and the health of your family by visiting your family dentist regularly.

Regular exams are an important part of maintaining your oral health. During your regular exam, we will:
- Check for any problems that you may not see or feel
- Look for cavities or any other signs of tooth decay
- Inspect your teeth and gums for gingivitis and signs of periodontal disease
- Perform a thorough teeth cleaning
Your regular exam will take about 45 minutes. Each regular exam includes a detailed teeth cleaning, in which we will clean, polish, and rinse your teeth to remove any tartar and plaque that have built up on the tooth’s surface.
Visiting our office every six months gives you the chance to talk to the doctor about any questions you may have about your oral health. Regular exams are offered by appointment only, so please contact our practice today to schedule your next dental exam and teeth cleaning.
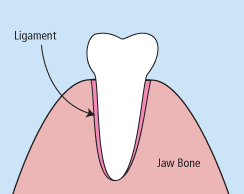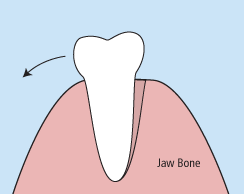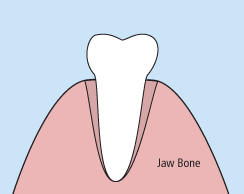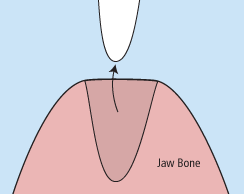
There are times when it is necessary to remove a tooth. Sometimes a baby tooth has misshapen or long roots that prevent it from falling out as it should, and the tooth must be removed to make way for the permanent tooth to erupt. At other times, a tooth may have so much decay that it puts the surrounding teeth at risk of decay, so your doctor may recommend removal and replacement with a bridge or implant. Infection, orthodontic correction, or problems with a wisdom tooth can also require removal of a tooth.
When it is determined that a tooth needs to be removed, your dentist may extract the tooth during a regular checkup or may request another visit for this procedure. The root of each tooth is encased within your jawbone in a “tooth socket,” and your tooth is held in that socket by a ligament. In order to extract a tooth, your dentist must expand the socket and separate the tooth from the ligament holding it in place. While this procedure is typically very quick, it is important to share with your doctor any concerns or preferences for sedation.
Once a tooth has been removed, neighboring teeth may shift, causing problems with chewing or with your jaw joint function. To avoid these complications, your dentist may recommend that you replace the extracted tooth.

Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is an infection of the gums surrounding your teeth. Gum disease is one of the top reasons for tooth loss in adults, and because it is virtually pain-free, many patients do not know they have the disease. During each regular checkup, your dentist will check for signs of periodontal disease by measuring the space between your teeth and gums.
What causes gum disease?
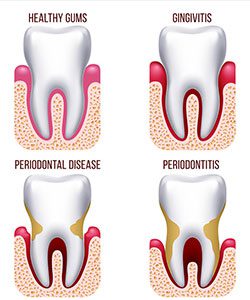
Gum disease is caused by a buildup of plaque (a sticky form of bacteria that forms on the teeth). If the plaque is not removed (by flossing, brushing, and regular dental checkups), it will continue to build up and create toxins that can damage the gums. Periodontal disease forms just below the gum line and creates small pockets that separate the gums from the teeth. Periodontal disease has two stages: gingivitis and periodontitis.
- Gingivitis — This is the early stage of gum disease, when the gums become red and swollen, and bleed easily. At this stage, the disease is treatable and can usually be eliminated by daily brushing and flossing.
- Periodontitis — If left untreated, gingivitis will advance into periodontitis, and the gums and bone that support the teeth will become seriously and irreversibly damaged. Gums infected with periodontitis can cause teeth to become loose, fall out, or be removed by a dentist.
Certain factors can increase a patient’s risk of developing periodontal disease, including:
- Smoking or using chewing tobacco
- Diabetes
- Certain types of medication such as steroids, anti-epilepsy drugs, cancer therapy drugs, calcium channel blockers, and oral contraceptives
- Bridges that no longer fit properly
- Crooked teeth
- Old fillings
- Pregnancy
While it is possible to have periodontal disease and not know it, some symptoms can include:
- Gums that bleed easily
- Red, swollen, tender gums
- Gums that have pulled away from the teeth
- Persistent bad breath or bad taste
- Pus between your teeth and gums
- Permanent teeth that are loose or separating
- Any change in the way your teeth fit together when you bite
- Any change in the fit of partial dentures
Treating gum disease
Treatments for gum disease can vary depending on the severity of each individual case. Typical treatments include:
- Non-surgical treatments such as at-home periodontal trays, and scaling and root planing (deep cleaning)
- Periodontal surgery and laser gum surgery
- Dental implants
Preventing gum disease
Regular dental checkups and periodontal examinations are important for maintaining your health and the health of your smile. You don’t have to lose teeth to periodontal disease, and by practicing good oral hygiene at home, you can significantly reduce your chances of ever getting gum disease. Remember to brush regularly, clean between your teeth, eat a balanced diet, and schedule regular dental visits to help keep your smile healthy.
Mouthguards
Whether you wear braces or not, protecting your smile while playing sports is essential. Mouthguards help protect your teeth and gums from injury. If you participate in any kind of full-contact sport, the American Dental Association recommends that you wear a mouthguard. Choosing the right mouthguard is essential. There are three basic types of mouthguards: the pre-made mouthguard, the “boil-and-bite” fitted mouthguard, and a custom-made mouthguard from your dentist. When you choose a mouthguard, be sure to pick one that is tear-resistant, comfortable and well-fitted for your mouth, easy to keep clean, and does not prevent you from breathing properly. Your dentist can show you how to wear a mouthguard properly and how to choose the right mouthguard to protect your smile.

Nightguards
If you often wake up with jaw pain, earaches, or headaches, or if you find yourself clenching or grinding your teeth, you may have a common condition called “bruxism.” Many people do not even know that they grind their teeth, as it often occurs when one is sleeping. If not corrected, bruxism can lead to broken teeth, cracked teeth, or even tooth loss.
There is an easy, non-invasive treatment for bruxism: nightguards. Nightguards are an easy way to prevent the wear and damage that teeth-grinding causes over time. Custom-made by your dentist from soft material to fit your teeth, a nightguard is inserted over your top or bottom arch and prevents contact with the opposing teeth.


If you’ve been diagnosed with gum disease, there are a variety of treatment options depending on the details of your situation and the severity of the problem. We always start with the least invasive options, which are non-surgical. However, in more serious cases, surgery may be necessary.
Non-surgical treatment
The first line of defense against gum disease is a unique type of cleaning called “scaling and root planing.” In this procedure, an ultrasonic cleaning device is used to remove plaque and tartar from your teeth where regular cleaning devices can’t reach: under the gum line, on the tooth, and around the root. Then, the rough surface of the tooth and the root are smoothed out (planed). This provides a healthy, clean surface that makes it easier for the gum tissue to reattach to the tooth.
If you address your gum disease before it becomes severe, scaling and root planing may be the only treatment you need. However, as with any dental procedure, after-care is vital. In order to keep your teeth in good shape and resist future occurrences of gum disease, you must brush and floss daily, eat a healthy diet, avoid tobacco use, and have regular dental checkups. Even after a successful scaling and root planing, if you don’t attend to your teeth properly, it’s quite likely that you’ll develop gum disease again.
Surgical treatment options
If the tissue or bone surrounding your teeth is too damaged to be repaired with non-surgical treatment, several surgical procedures are available to prevent severe damage and to restore a healthy smile. We will recommend the procedure that is best suited to the condition of your teeth and gums. Following is a list of common types of periodontal surgery:
- Pocket Depth Reduction
In a healthy mouth, the teeth are firmly surrounded by gum tissue and securely supported by the bones of the jaw. Periodontal disease damages these tissues and bones, leaving open spaces around the teeth that we call pockets. The larger these pockets are, the easier it is for bacteria to collect inside them, leading to more and more damage over time. Eventually the supportive structure degrades to the point that the tooth either falls out or needs to be removed.During pocket reduction procedures (also known as “flap surgery”), we fold back the gum tissue and remove the bacteria hiding underneath, as well as the hardened plaque and tartar that have collected. We may also remove any tissue that is too damaged to survive. We then sew the healthy tissue back into place. Now that the tooth and root are free of bacteria, plaque, and tartar, and the pockets have been reduced, the gums can reattach to the teeth. - Regeneration
When the bone and tissue supporting the teeth have been lost due to severe gum disease, we can restore these areas with a regeneration procedure. During this process, we begin by folding back the gum tissue and removing the bacteria, plaque, and tartar. Depending on your situation, we may then perform a bone graft to stimulate new bone growth, or we may apply a special kind of protein that stimulates tissue growth to repair the areas that have been destroyed by the disease. - Soft-Tissue Graft
A frequent symptom of gum disease is gum recession (also called gingival recession). As the gums recede, more of the roots are revealed. This can make teeth appear longer and can also create sensitivity to hot or cold liquids or food. It also exposes the tooth to increased damage from gum disease, as bacteria, plaque, and tartar attack the surface of the tooth and the root.During a soft-tissue graft, tissue from the top of your mouth or another source is sewed to the gum area, covering the roots and restoring the gum line to its original, healthy location. This procedure can also be performed for cosmetic reasons.
